Dapr Event Bridge
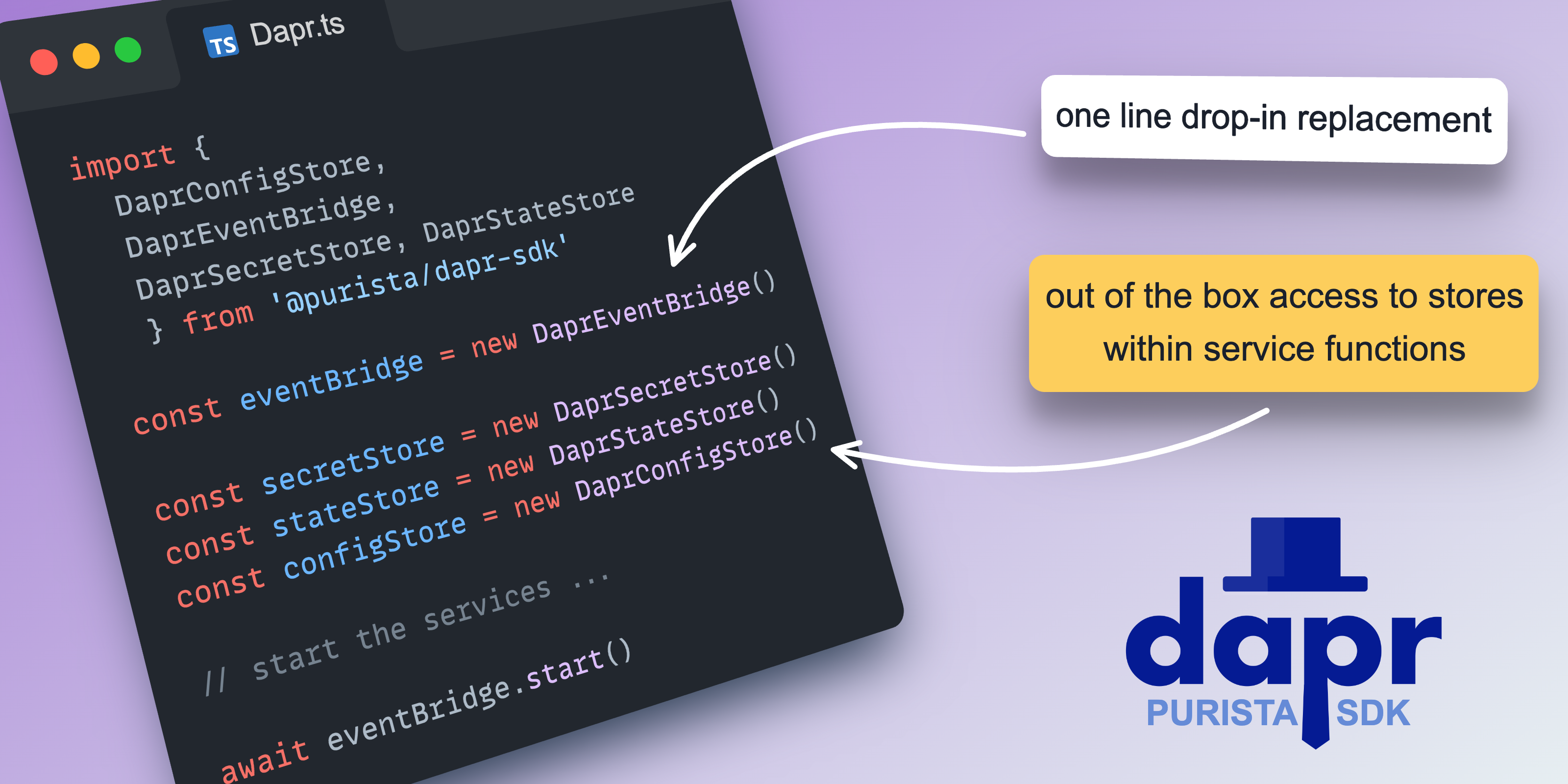
@purista/dapr-sdk provides a Dapr-oriented bridge and adapters for Dapr component-based stores.
Delivery semantics
Semantics are driven by the selected Dapr pub/sub component and broker backend.
- typical mode: component-dependent (many setups are at-least-once)
- durability: component-dependent
- retries/dead-lettering: component and resiliency policy dependent
Always verify your concrete component behavior in integration tests.
Stream support
PURISTA stream runtime (openStream) is currently not implemented for Dapr bridge.
Startup order
Use the startup sequence required for Dapr endpoint discovery:
- create Dapr bridge (not started)
- create/start service instance
- start Dapr bridge
Reliability recommendations
- document and version-control Dapr component/resiliency specs
- validate duplicate handling in command/subscription side effects
- test sidecar restarts and service readiness ordering
